(543)
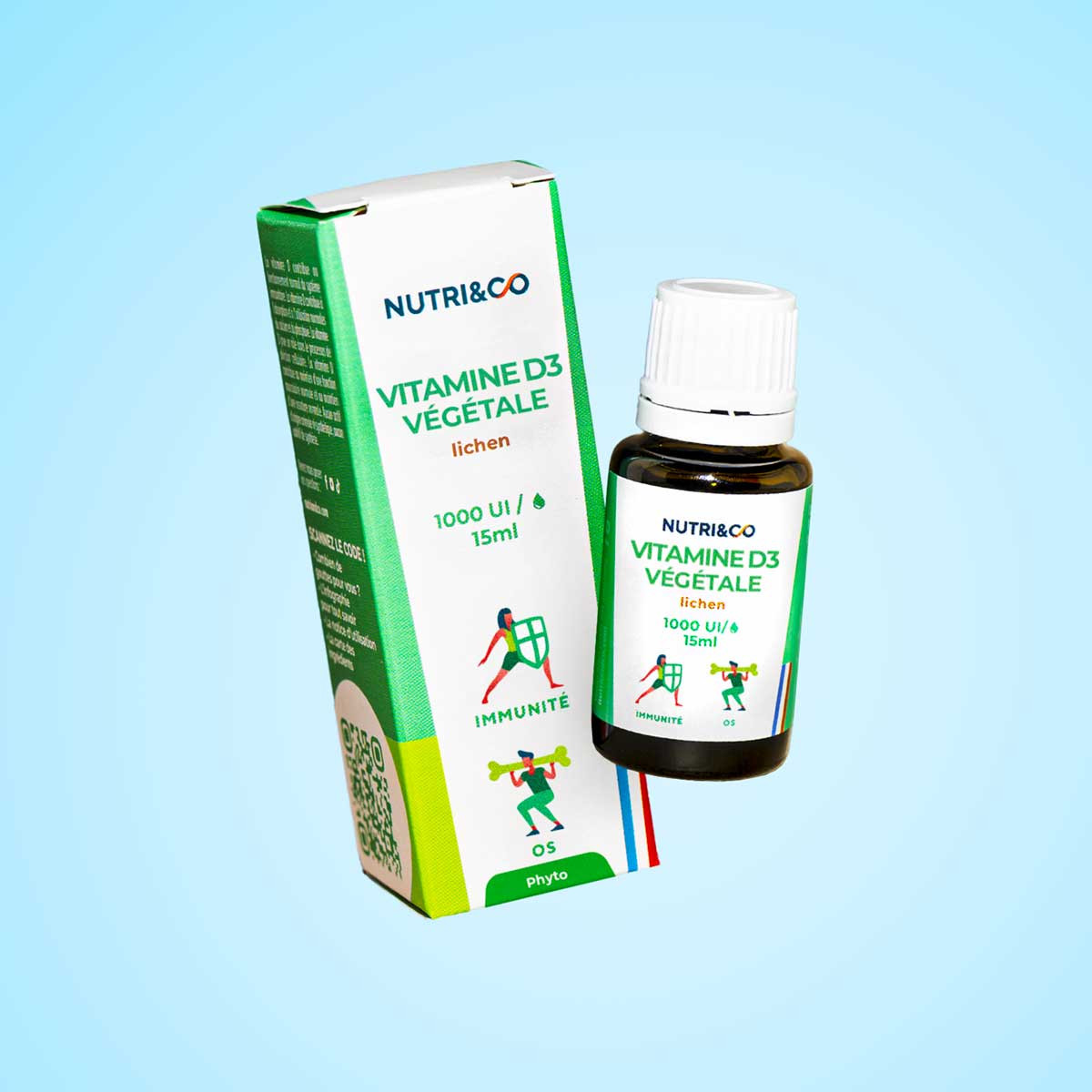
Vegetable Vitamin D
€19.90
Vitamin D is essential for our bone health and for the strength of our immune system. However, 6 out of 10 French people are deficient in vitamin D, and 1 to 2 out of 10 people have a proven deficiency.
Extracted from Lichen Boréal, our vegetable vitamin D3 is integrated into extra virgin rapeseed oil for optimal absorption. With a dosage of 1000 IU per drop, it is ideal for daily use and for the whole family (from 4 years old). View more
Vegetable Vitamin D
€19.90
Paiement
sécuriséLivraison offerte
dès 69€ d'achatLivraison
en 48hParrainer
un procheRécompenses
fidélité








